US can't reverse re

Shi Yu/China Daily。
The world is watching closely as the United States and China engage in high-stakes bilateral trade negotiations. While the immediate outcomes may be modest tariff adjustments or managed market access in selected sectors, those can be best understood as tactical responses to deeper structural tensions rather than strategic breakthroughs. The broader implications for global trade lie not in the specifics of such negotiations but in the shifts they signify: away from multilateralism and US dollar hegemony, and toward a new, multipolar global trade architecture.。
At the heart of the current tensions is the US' growing anxiety over its relative decentering. Having enjoyed more than three decades of the unrivalled global hegemony since the end of the Cold War, the US now finds itself challenged by China's rising technological prowess, industrial scale and global integration. Under the Donald Trump administration, the US' anxiety has transformed into an explicitly transactional, bilateral trade posture.。
The US has been increasingly dismissing multilateral institutions — for long the instruments through which Washington shaped global norms and gained geopolitical advantage — in favor of "deal-making" with individual countries, and projected this bilateralism, steeped in zero-sum logic, as strength. By doing so, it has exposed its strategic incoherence.。
For example, through its trade policy, the US administration tried to simultaneously increase domestic manufacturing output — by penalizing imports — and maintain the dollar's status as the global reserve currency. These goals are not easily reconciled. A strong global reserve currency fuels persistent trade deficits. Penalizing imports through tariffs does disrupt this dynamic but not without costs. If the US were to genuinely reindustrialize at scale, it would need to import huge volumes of capital goods and intermediate inputs, exacerbating the very trade deficit it seeks to narrow. The paradox is that narrowing the trade deficit would first require widening it.。
The alternative is simply to reduce overall aggregate demand in the economy by slashing public expenditure. That doesn't look like happening.。
More fundamentally, the hollowing out of US manufacturing was never principally a result of trade agreements. It was a symptom of a deeper reorientation of US capital. Over the past four decades, US capital has been progressively reallocated from industrial production to financial engineering, creating asset bubbles, stock buybacks and speculative real estate investment. Wall Street flourished as "Main Street" faded. The share of GDP derived from financial services soared, while fixed capital formation in manufacturing stagnated. Reversing this trend would require reducing the political and institutional power of finance, an unpalatable proposition for any administration.。
Yet the US still manufactures products such as high-end equipment and advanced electronics, and develops or advances technologies like aerospace technology and military technology. But their production is capital-intensive, not labor-intensive, and they don't fill the physical or emotional void created by the offshoring of everyday consumer goods manufacturing that began in the 1970s. The sense of economic alienation among broad swathes of the American working class is as much cultural as it is economic. Tariffs may meet some symbolic need for control or retribution, but they cannot restore the industrial base to its past state.。
Also, the rest of the world is adapting to the US' contradictions. The weaponization of the dollar, through sanctions and arbitrary financial restrictions, has catalyzed a slow but deliberate move toward alternatives. Some emerging economies are accelerating trade settlements in their national currencies and exploring alternative clearing mechanisms. ASEAN member states, on the other hand, are reducing their reliance on the dollar in regional trade, particularly with China, Japan and the Republic of Korea.。
Even the oil-rich Gulf Cooperation Council member states are diversifying their trade currency strategies. The demand for the dollar as a trade settlement medium is gradually diminishing, which the European Central Bank sees as an opportunity for the euro to play a more prominent role in global trade. This fragmentation is not a retreat from but a reconfiguration of globalization.。
The new globalization that is emerging is multipolar in character, regional in structure and decentralized in operations. Institutions such as the World Trade Organization will likely persist, offering an overarching framework for administrative and policy guidance. But much of the practical work of trade governance — harmonization of standards, digital commerce rules and investment arbitration — will occur in regional and bilateral forums. In this regard, the US-China negotiations are not anomalous but emblematic.。
For many countries, especially in the Global South, the US' retreat from multilateralism poses risks but also creates new space. The growing importance of South-South trade, supported by new infrastructure financing and currency swap arrangements, is reducing the Global South's dependence on Western markets and institutions, with the Belt and Road Initiative creating corridors of trade and production that bypass traditional Western trade bottlenecks.。
The US remains a major consumer market, responsible for about 14 percent of global imports. But its share in the global economy is declining, reflecting both its waning economic clout and the diversification of global demand. For exporters, aligning with the new regional poles of growth — in East Asia, South Asia and parts of Africa — will become increasingly important. And supply chains will be restructured to hedge against geopolitical volatility, balancing proximity, cost and political risk.。
The Sino-US trade tango should not be seen as the primary determinant of the future of global trade. Rather, it is a mirror of the broader historical shift: from unipolarism to multipolarism, from dollar dominance to currency diversification, from multilateralism to mosaic regionalism. The world isn't de-globalizing; it is re-globalizing on new terms and under new rules.。
The author is an adviser to former Australian prime minister Kevin Rudd, adjunct professor at Queensland University of Technology and a senior research fellow at Taihe Institute.。
The views don't necessarily reflect those of China Daily.。
(责任编辑:热点)
-
八部分联合发文 到2030年培养100家左右全国数智供应链领军企业
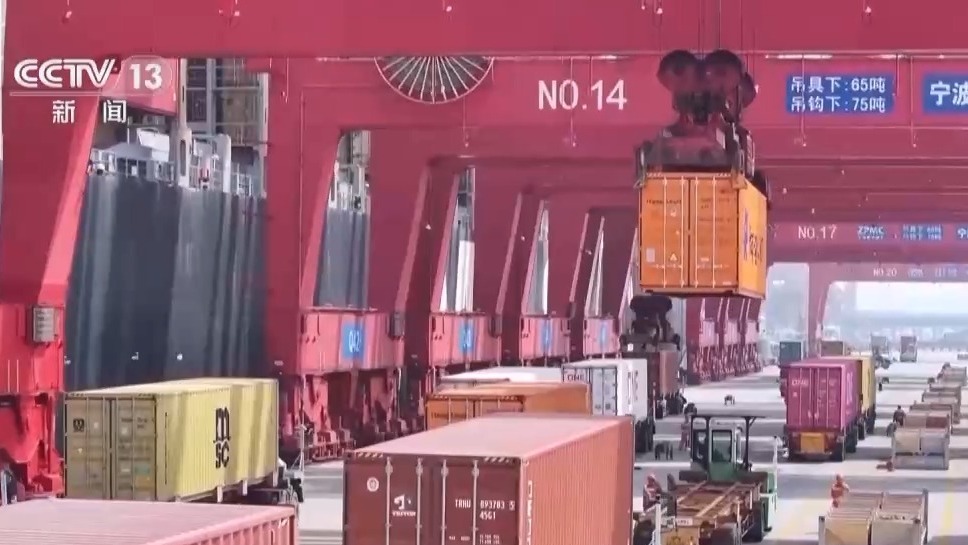 今日5月26日),商务部、国家展开变革委等8部分发布《加速数智供应链展开专项举动计划》,清晰在农业、制造业、批发业、零售业等要点范畴加速数智供应链展开。,推进下降全社会物流本钱,培养一批数智供应链领军
...[详细]
今日5月26日),商务部、国家展开变革委等8部分发布《加速数智供应链展开专项举动计划》,清晰在农业、制造业、批发业、零售业等要点范畴加速数智供应链展开。,推进下降全社会物流本钱,培养一批数智供应链领军
...[详细]
-
岚图轿车与清华大学牵手共建研制技能中心 加速人工智能技能车端使用
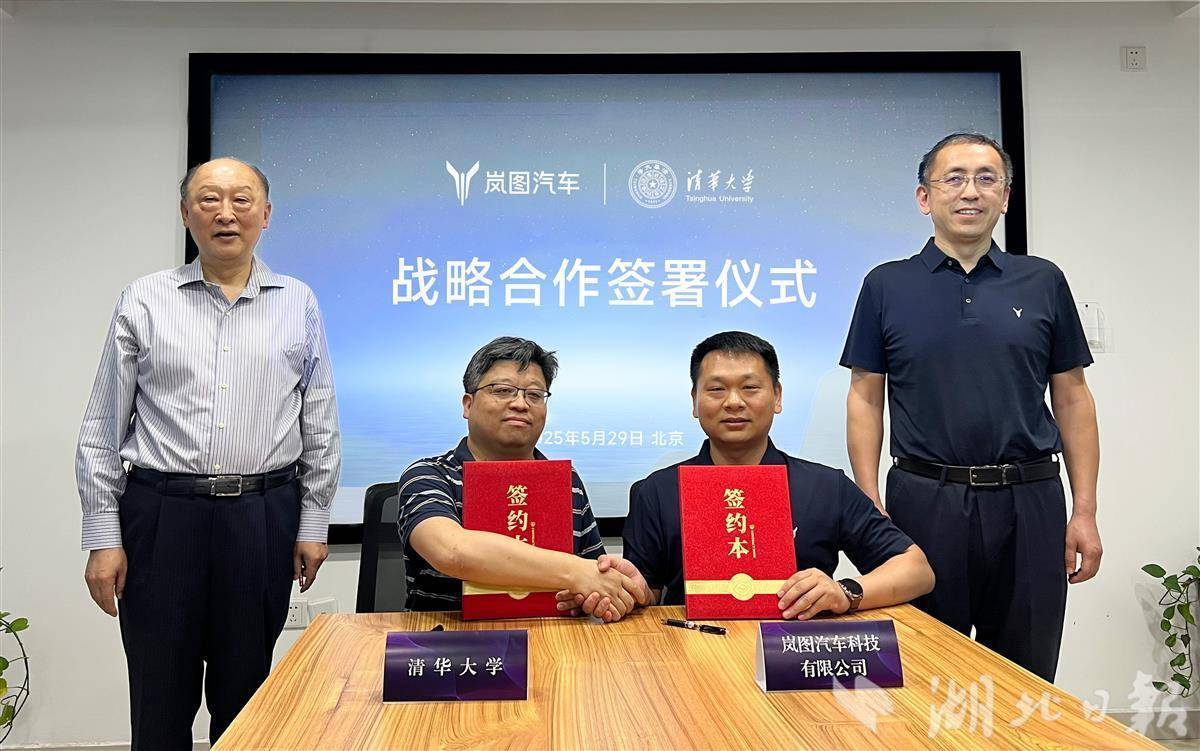 湖北日报讯记者左晨)5月29日,岚图轿车与清华大学正式签署战略协作结构协议,两边将中心聚集人工智能范畴,打开深度战略协作。未来,岚图与清华将联手布局人工智能,在智能网联轿车技能研制、人才培养、效果转化
...[详细]
湖北日报讯记者左晨)5月29日,岚图轿车与清华大学正式签署战略协作结构协议,两边将中心聚集人工智能范畴,打开深度战略协作。未来,岚图与清华将联手布局人工智能,在智能网联轿车技能研制、人才培养、效果转化
...[详细]
-
 极目新闻记者 陈勇。通讯员 易荣波 李怡。5月29日,“大别山上红旗飘”武汉6所高校大学生国旗护卫队展现邀请赛在孝感市大悟县举行。来自武汉的华中科技大学、华中农业大学、江汉大学、武汉传媒学院、武汉文理
...[详细]
极目新闻记者 陈勇。通讯员 易荣波 李怡。5月29日,“大别山上红旗飘”武汉6所高校大学生国旗护卫队展现邀请赛在孝感市大悟县举行。来自武汉的华中科技大学、华中农业大学、江汉大学、武汉传媒学院、武汉文理
...[详细]
-
 湖北日报讯记者冯袁玥、通讯员王瓒)“端午将至,大雨却来了”“端午要落空了!”交际网络上不少游客宣布如此感叹。据了解,为保证游客玩耍安全、保证玩耍体会,东湖听涛景区将5月31日起启幕的端午文明节中的野外
...[详细]
湖北日报讯记者冯袁玥、通讯员王瓒)“端午将至,大雨却来了”“端午要落空了!”交际网络上不少游客宣布如此感叹。据了解,为保证游客玩耍安全、保证玩耍体会,东湖听涛景区将5月31日起启幕的端午文明节中的野外
...[详细]
-
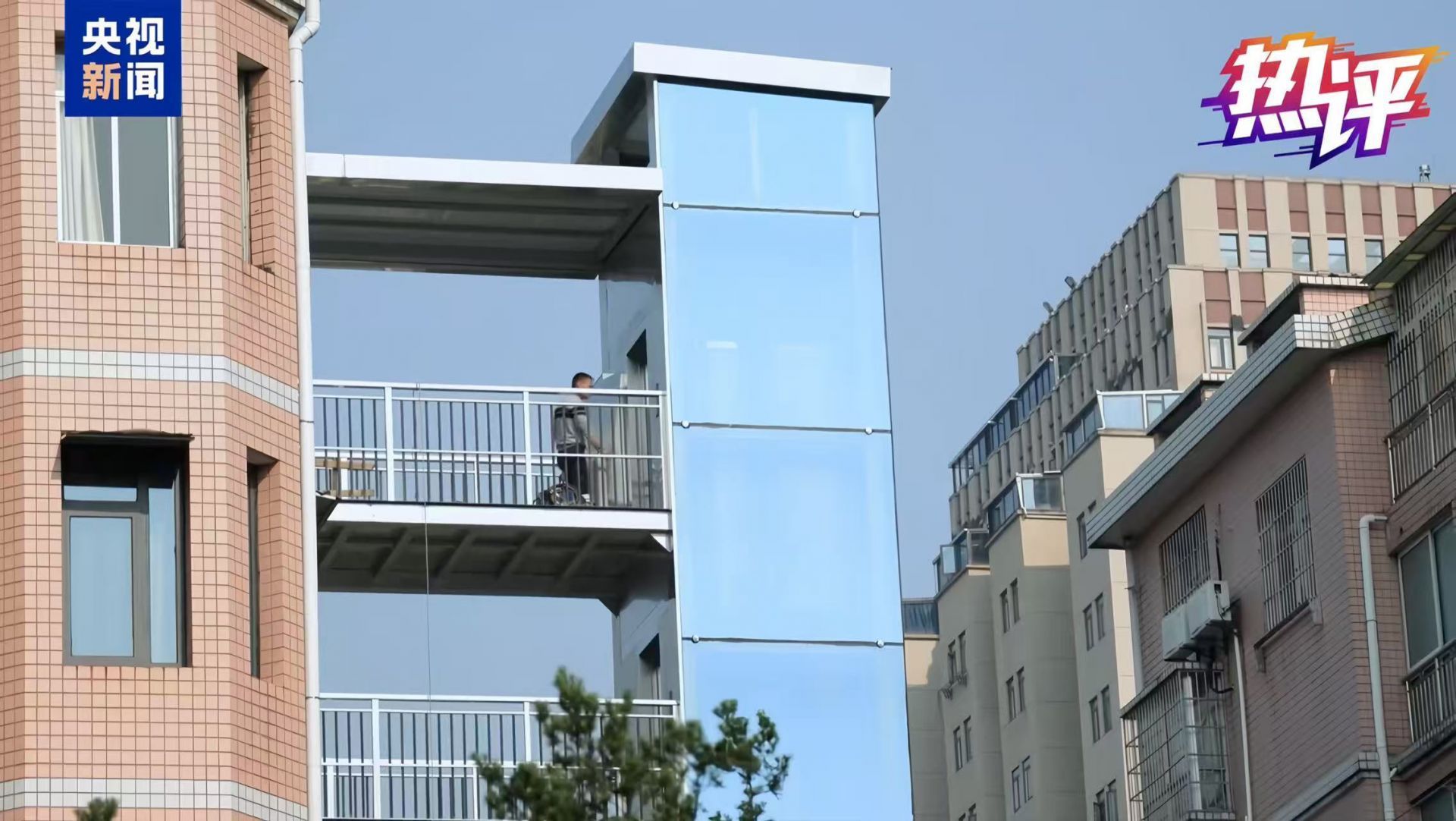 墙体开裂、户型差、常常漏水……始建于上世纪70年代的北京市桦皮厂8号楼曾是典型的“老破小”,现在通过优化规划、旧址重建,不只户内面积增加了、两房变三房,公共区域还增设了电梯和适老化设备,引得居民们拍案
...[详细]
墙体开裂、户型差、常常漏水……始建于上世纪70年代的北京市桦皮厂8号楼曾是典型的“老破小”,现在通过优化规划、旧址重建,不只户内面积增加了、两房变三房,公共区域还增设了电梯和适老化设备,引得居民们拍案
...[详细]
-
 近期,网信部分深化安排展开“明亮清明·整治短视频范畴歹意营销乱象”专项举动,辅导短视频服务渠道以及供给短视频功用的渠道从严整治歹意营销杰出问题,依法依约处置一批违法违规账号。现将部分典型事例通报如下:
...[详细]
近期,网信部分深化安排展开“明亮清明·整治短视频范畴歹意营销乱象”专项举动,辅导短视频服务渠道以及供给短视频功用的渠道从严整治歹意营销杰出问题,依法依约处置一批违法违规账号。现将部分典型事例通报如下:
...[详细]
-
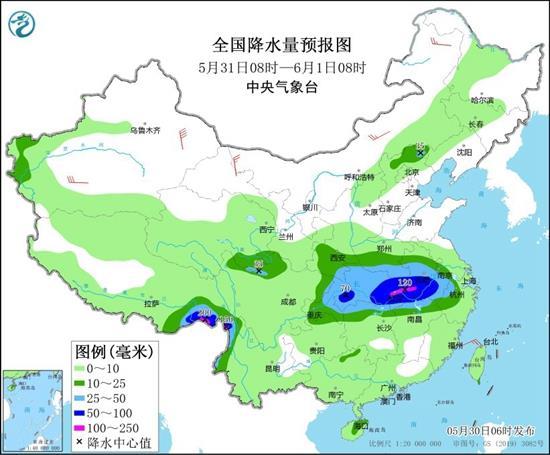 今日5月30日)开端至6月2日,中东部新一轮较大规模降雨逐渐上线,长江中下游一带将为中心影响区域,局地有大暴雨伴有强对流。大众出行需及时重视预警预告信息,端午假日不要前往山区等地质灾祸易发地带玩耍。5
...[详细]
今日5月30日)开端至6月2日,中东部新一轮较大规模降雨逐渐上线,长江中下游一带将为中心影响区域,局地有大暴雨伴有强对流。大众出行需及时重视预警预告信息,端午假日不要前往山区等地质灾祸易发地带玩耍。5
...[详细]
-
 近来,一场由武汉市城市管理法律委员会精心组织的“i武汉i家乡”清洁家乡举动在全市范围内打开。城管、园林、水务、环保等多部分打破壁垒全力协作,各机关企事业单位、各区城管局、广阔志愿者积极参加,掀起了全域
...[详细]
近来,一场由武汉市城市管理法律委员会精心组织的“i武汉i家乡”清洁家乡举动在全市范围内打开。城管、园林、水务、环保等多部分打破壁垒全力协作,各机关企事业单位、各区城管局、广阔志愿者积极参加,掀起了全域
...[详细]
-
 5月25日是国际甲状腺日。甲状腺作为人体重要的内分泌器官,其健康与年纪、遗传、环境等要素密切相关,但更易被忽视的是日常习气的影响。怎么经过科学的生活方式保护甲状腺功用?为此,人民网采访了西安交通大学榜
...[详细]
5月25日是国际甲状腺日。甲状腺作为人体重要的内分泌器官,其健康与年纪、遗传、环境等要素密切相关,但更易被忽视的是日常习气的影响。怎么经过科学的生活方式保护甲状腺功用?为此,人民网采访了西安交通大学榜
...[详细]
-
 2025年高考接近,一些不法分子受利益唆使,分布高考相关虚伪信息,制造贩卖焦虑,组织施行欺诈,乃至诱导考生做弊,严峻危害考生和家长切身利益,严峻打乱考试招生次序。为此,教育部会同相关部分整理汇总了近年
...[详细]
2025年高考接近,一些不法分子受利益唆使,分布高考相关虚伪信息,制造贩卖焦虑,组织施行欺诈,乃至诱导考生做弊,严峻危害考生和家长切身利益,严峻打乱考试招生次序。为此,教育部会同相关部分整理汇总了近年
...[详细]
 媒体大咖看新疆丨领会现代农业和中医文明的魅力
媒体大咖看新疆丨领会现代农业和中医文明的魅力 俗人微光|今世科研人的“硬核浪漫”
俗人微光|今世科研人的“硬核浪漫” 《智能大坝理念与实践》出版发行
《智能大坝理念与实践》出版发行 特写:多哈赛场的两层邂逅——新华社记者与孙颖莎先后偶遇巴赫
特写:多哈赛场的两层邂逅——新华社记者与孙颖莎先后偶遇巴赫
